User Tools
Table of Contents
OpenSSH for Windows
Installation
Requirements
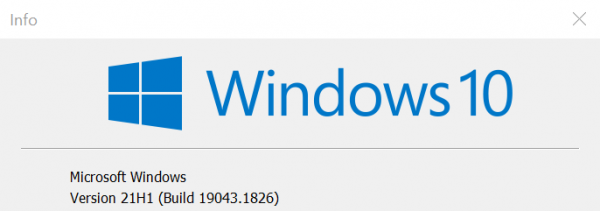
Make sure you use Windows Build 1809 or newer, you can check this by executing the following command via WIN + R
winver
If this is the case, choose one of the following installation methods.
Installation GUI
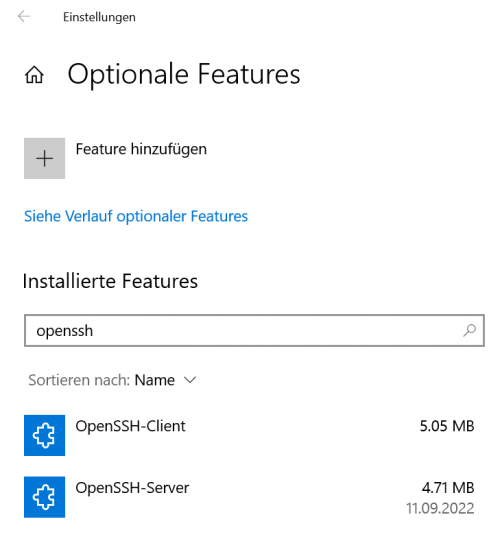
Go to Settings → Apps → Apps and features → Optional features
or run the following command via WIN + R
ms-settings:appsfeatures
Click on “Add feature” and search for “openssh”, then install “OpenSSH Server”
Installation PowerShell "Add"
Open PowerShell as Admin
# Install the OpenSSH Server Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name OpenSSH.Server~~~~0.0.1.0 # (Optional) Install the OpenSSH Client Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name OpenSSH.Client~~~~0.0.1.0
Source: docs.microsoft.com - Get started with OpenSSH for Windows (EN)
Installation PowerShell "dism"
Open PowerShell as Admin
dism /Online /Add-Capability /CapabilityName:OpenSSH.Server~~~~0.0.1.0
Add to autostart
Open PowerShell as Admin
# Start the sshd service Start-Service sshd # OPTIONAL but recommended: Set-Service -Name sshd -StartupType 'Automatic'
Check installation
GUI
Go to Settings → Apps → Apps and features → Optional features
or run the following command via WIN + R
ms-settings:appsfeatures
OpenSSH Server should be listed as “installed feature”
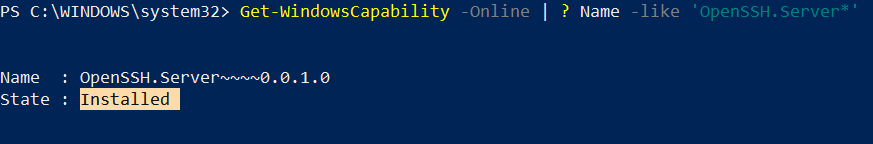
PowerShell
Configuration
Open port 22 on Windows Firewall
Usually the port will be opened when installing OpenSSH, to check if its opened and add if not, execute the following code via PowerShell (admin)
if (!(Get-NetFirewallRule -Name "OpenSSH-Server-In-TCP" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | Select-Object Name, Enabled)) {
Write-Output "Firewall Rule 'OpenSSH-Server-In-TCP' does not exist, creating it..."
New-NetFirewallRule -Name 'OpenSSH-Server-In-TCP' -DisplayName 'OpenSSH Server (sshd)' -Enabled True -Direction Inbound -Protocol TCP -Action Allow -LocalPort 22
} else {
Write-Output "Firewall rule 'OpenSSH-Server-In-TCP' has been created and exists."
}
Allow/Deny users

Add publickey to authorized_keys

Troubleshooting
Username or Password wrong